Fertility testing, which involves sperm testing for men and a variety of tests for women, is essential if you’re having trouble conceiving. It can also give you valuable information about your overall health. But how did modern fertility testing come to be?
We look into the history of fertility testing, the different types of fertility testing, including sperm testing and semen analysis, and the benefits and costs of testing, to help you understand whether fertility testing is right for you.
Key takeaways
- Fertility testing assesses your fertility and helps you understand areas that could use treatment or improvement.
- The practice of fertility testing has its roots in the discovery of sperm in the 1600s and has since evolved significantly.
- Fertility testing generally involves a semen analysis and sperm testing for people with sperm and hormone tests, blood tests, or imaging tests for people with ovaries.
- Legacy offers at-home sperm testing kits to help you understand your fertility and gain insights into your overall health.
What is fertility testing?
If you’re experiencing trouble conceiving a child after 6 to 12 months of trying, fertility testing may be used to help identify the source of the issue. Around 40 to 50% of infertility cases are caused by male-factor infertility, and male fertility testing may help pinpoint the source of the problem.
For people with sperm, male fertility testing will involve a semen analysis and sperm testing. Semen analyses examine the quality of your semen (the white fluid the penis releases during ejaculation) and the sperm it contains to help evaluate your fertility. In particular, the semen analysis and sperm testing looks at the following areas and compares them against standard parameters:
Abnormal results of the semen analysis and sperm testing could indicate problems with your sperm that could affect your ability to conceive a child. This knowledge may help you and your doctor address an underlying medical source of the problem or lead you to change certain lifestyle habits to improve your sperm health and, hopefully, your fertility.
Fertility testing: a brief history
While sperm was first observed in the 1600s, it took hundreds of years and contributions from many researchers to understand human fertilization and develop fertility testing along with fertility treatments.
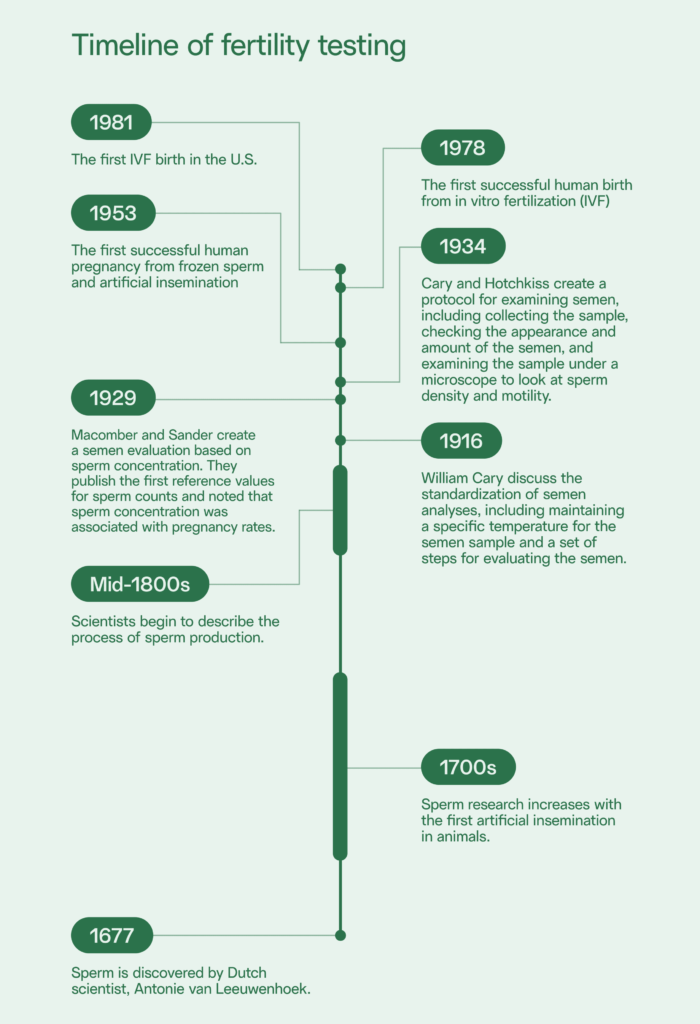
When was sperm first discovered?
Sperm was originally discovered in 1677 by Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. Research into sperm increased in the 1700s, with the first artificial insemination in animals, and scientists began to describe the process of sperm production in the mid-1800s.
When did semen analysis begin?
Many researchers contributed to the development of the modern semen analysis and sperm testing. During the early 1900s, much of this work focused on studying sperm from both humans and animals, including sperm counts, movement, and shape.
Notably, in 1916, William Cary discussed the standardization of semen analyses and sperm testing, including maintaining a specific temperature for the semen sample and a set of steps for evaluating the semen.
In 1929, Macomber and Sander created a semen analysis based on sperm concentration. Following a study of nearly 300 men, they published the first reference values for sperm counts and noted that sperm concentration was associated with pregnancy rates.
Subsequently, in 1934, Cary and Hotchkiss created a protocol for examining semen, including collecting the sample, checking the appearance and amount of the semen, and examining the sample under a microscope to look at sperm density and motility.
While improvements to semen analyses continued, the test has been used to assess infertility since the early 1930s.
When did fertility treatment start?
Fertility treatment has its roots in the late 1700s with the discovery that an egg must make contact with the sperm to create an embryo, followed by successful artificial insemination of animals.
While artificial insemination started being used on people in the late 1770s, the modern practice largely started in the 1940s. This was followed by the first successful human pregnancy from frozen sperm and artificial insemination in 1953 and the first successful human birth from in vitro fertilization (IVF) in 1978 in the UK. The first IVF birth took place in the U.S. in 1981 and the method is now responsible for between 1 and 3% of births in the U.S. and Europe each year.
Why consider fertility testing?
A main reason to consider fertility testing is if you’ve been trying to get pregnant for one year (or six months if the partner with ovaries is age 35 or above) without success.
Even if you’re not trying to conceive, fertility testing may be helpful to look for areas that could use improvement or to gain insights into your health as a whole.
If you choose to freeze your sperm, you’ll also get a semen analysis to check the health and viability of your sperm.
Conversely, you’ll need to test your fertility to check for the presence of sperm after a vasectomy, to confirm the operation was successful and you’re no longer fertile.

Types of fertility testing
Fertility testing often starts with an infertility checkup, which includes a physical exam and a discussion of each partner’s health and sexual history.
For people with sperm, male fertility testing mainly involves a semen analysis and sperm testing. Semen analysis should be done even if the individual has previously conceived a child. Fertility testing may also include checking hormone levels through blood tests and performing an ultrasound of the scrotum to look for issues in the testicles.
Fertility testing for people with ovaries is less straightforward and may involve:
- checking ovulation, either by tracking it at home, performing an ultrasound of the ovaries, or ordering blood tests
- using blood tests to check hormone levels related to fertility, including follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and inhibin-B
- checking for other health conditions that could affect fertility, like thyroid disorders and hyperprolactinemia
- performing a hysterosalpingogram (an x-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes) to check for any blockages that could be preventing the movement of the egg or sperm
- performing a laparoscopy, which involves inserting an instrument called a laparoscope through a small cut in the abdomen to check the ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes for problems such as endometriosis
Benefits of fertility testing
Fertility testing can help you understand your fertility, identify problems that may be preventing you from conceiving, and give you the information needed to treat or improve your fertility. It may also inform you of underlying conditions that could be affecting other areas of your health.
You don’t need to go into fertility testing expecting a negative outcome. If your test returns normal results, that’s all the better for giving you peace of mind about your fertility and overall health.
Fertility testing costs
According to a 2020 study, the average cost of a semen analysis was $161 from clinics that made pricing information available. However, prices aren’t always listed, and male fertility testing at conventional clinics often costs $250 or more.
Legacy offers a comprehensive at-home semen analysis and at-home sperm testing kits for $295, and it may be covered by your insurance, depending on your provider.
Legacy’s at-home sperm testing kits
With convenient and affordable options for male fertility testing, there’s no reason to wonder about your fertility. You can do sperm testing at home using Legacy’s at-home sperm testing kits. Simply order the at-home sperm testing kit, collect and send your sample, then receive the results about your fertility.