Hormones are chemical messengers that affect functions throughout your body, from bone mass to sperm production. Understanding male hormones can help you better understand your fertility. We take a look at the main male fertility hormones, how hormonal imbalances can affect your ability to conceive a child, and the benefits of hormonal testing for imbalances.
Key takeaways
- Hormones affect all parts of the male body, including fertility. High or low levels of certain hormones may affect your ability to conceive a child.
- Hormonal testing can show whether your hormones are in balance and provide insights into your fertility.
- If you and your partner want to build your family or are having trouble conceiving, hormonal testing for males alongside semen analysis might be the next step.
Hormones and male fertility
A variety of hormones play an important role both in general male health and in male fertility. These hormones work together and individually to influence sperm health, sexual characteristics, and more.
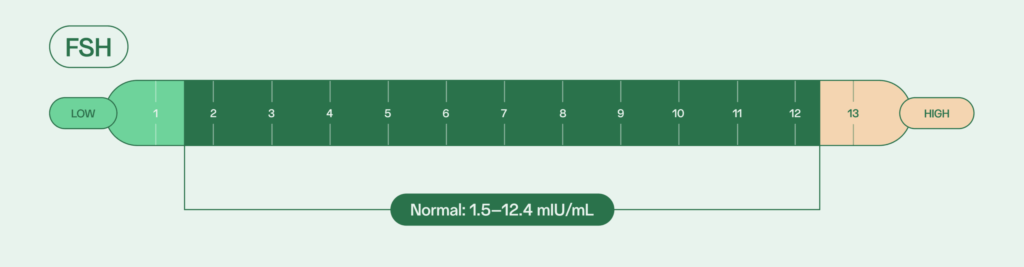
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is produced by the pituitary gland underneath your brain and is among the hormones analyzed when testing for hormonal imbalances. The pituitary is prompted to produce FSH via gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the region of your brain called the hypothalamus.
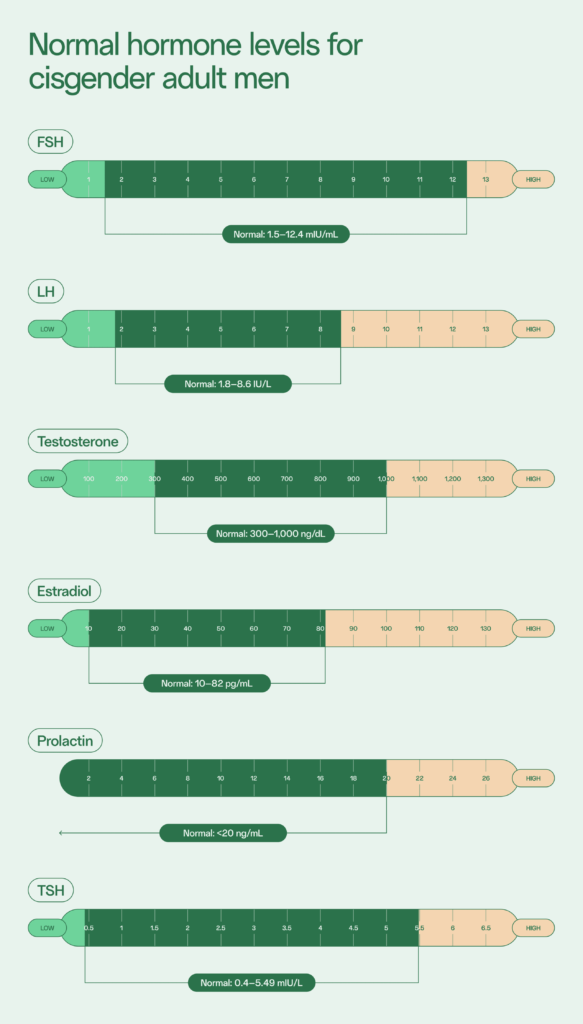
In males, FSH plays an essential role in starting and maintaining spermatogenesis (sperm production). Normal FSH levels for adult males is between 1.5 and 12.4 mIU/mL.
Low FSH on male hormone testing
If hormonal testing reveals you have low FSH, you may have an issue with the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Low FSH reduces both sperm count and sperm quality in men, and can help explain oligospermia (low sperm count) or other male-factor infertility issues.
High FSH on male hormone testing
High FSH on hormonal testing may indicate that FSH isn’t having the proper effect on your testes, and perhaps that an issue with the testicles is impairing sperm production. This could suggest damage to the testicles from an infection or a treatment like chemotherapy, or indicate that your sexual development has been affected by Klinefelter syndrome. This can also be highlighted when testing for hormonal imbalances.
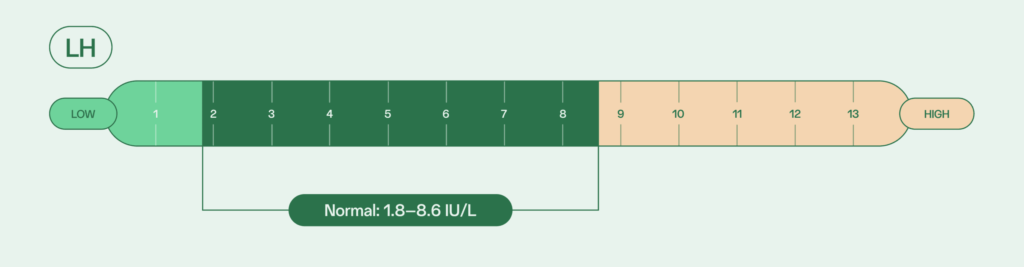
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Like FSH, luteinizing hormone (LH) is produced by the pituitary gland and is another integral male fertility hormone. Both male fertility hormones work together to direct sexual functions, and changes in their levels often occur together because they’re released from the same gland.
LH stimulates the testicles to produce testosterone, an important component in sperm production. Earlier on, LH also plays a role in puberty, specifically in developing sexual characteristics. Normal LH levels for adult males is between 1.8 and 8.6 IU/L; abnormal levels can be detected when testing for hormonal imbalances.
Low LH on male hormone testing
Low levels of LH could suggest a pituitary gland or hypothalamus disorder, or indicate that you have a genetic disorder called Kallmann syndrome. Left untreated, the lack of LH can lead to infertility and low testosterone levels.
High LH on male hormone testing
High LH levels may indicate damage to the testicles from radiation therapy or an infection. Alternatively, it may be a result of having Klinefelter syndrome, another genetic condition.
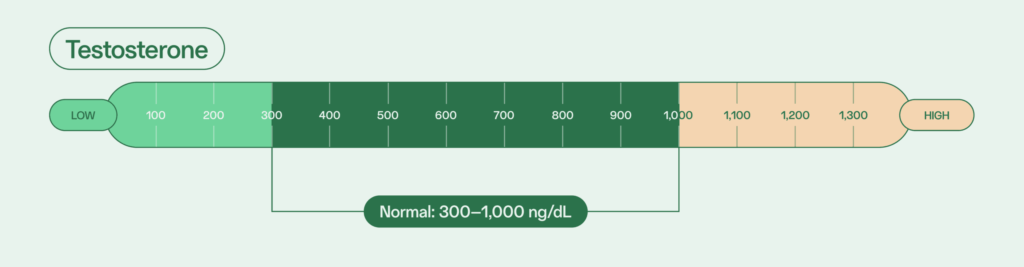
Testosterone
The sex hormone testosterone is produced by Leydig cells in the testicles in response to LH. Testosterone affects many parts of the male body, including:
- sex drive (libido)
- fertility
- sperm production
- sexual development
- amount of body fat
- bone mass
Normal testosterone levels for adult males are between 300 and 1,000 ng/dL. In general, testosterone decreases as you age and plays an essential role as a male fertility hormone.
Low T on male hormone testing
Low T, or hypogonadism, typically occurs when testosterone is measured at less than 300 ng/dL in the blood. It can result from aging, medications, diet, chemotherapy, genetic conditions, and cryptorchidism (undescended testicles), among other causes.
Low testosterone can lead to symptoms such as:
- erectile dysfunction
- low sex drive
- low sperm count
- smaller testicle size
- decreased muscle mass
- reduced bone mass
- more body fat
- trouble sleeping
- difficulty concentrating
- depression
High T on male hormone testing
Testosterone overproduction may occur if you have Cushing syndrome (a disorder where your body produces too much of the hormone cortisol over a sustained period) or a tumor in the testicles. It can lead to early puberty in younger people.
Taking external testosterone, in the form of testosterone therapy or anabolic steroids, can also raise the level of T in the blood. Any external testosterone can disrupt the natural balance of testosterone, FSH, and LH in the body, significantly impacting sperm production.
Estrogen
Estrogen is often considered a female hormone, but it’s also an important male fertility hormone. In cisgender men, around 20% of estrogen is produced by the testes, with the rest produced as the brain, skin, and bones converts testosterone to estrogen.
The main form of estrogen is called estradiol, and it can affect:
- fertility
- sex drive
- sperm production
- cholesterol levels
- muscle mass
- blood sugar
- cognitive function
- collagen production
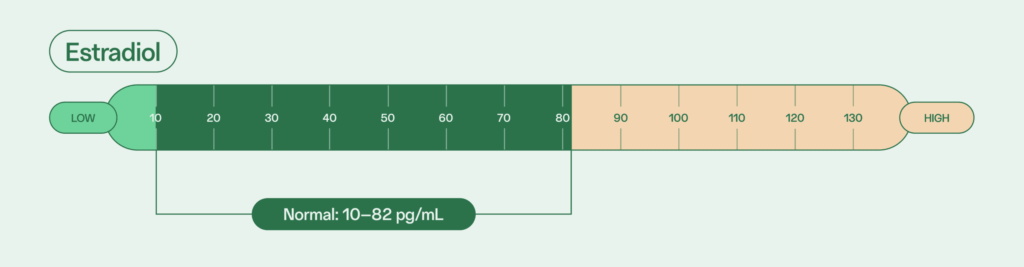
Normal estradiol levels for adult males is between 10 and 82 pg/mL.
Low estrogen on male hormone testing
Low levels of estrogen in men can cause:
- increased belly fat
- reduced sex drive
- low bone density
One of the primary causes of low estrogen is actually low testosterone, since T converts to estrogen in the male body.
High estrogen on male hormone testing
Overly high amounts of estrogen in men may lead to:
- erectile dysfunction
- infertility
- enlarged breasts
- prostate cancer
High estrogen levels may be caused by factors including excess body fat, liver issues, and stress.
Prolactin
In addition to other male fertility hormones, the pituitary gland also produces prolactin. Prolactin is the hormone that drives lactation in pregnant and postpartum people. For males, it enhances the effect of LH in the testes, aiding in testosterone production.
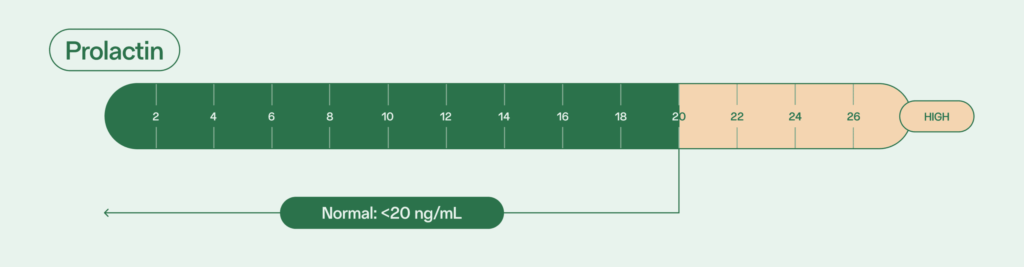
Dopamine and estrogen control the release of prolactin, although levels of this hormone in people with sperm are typically low. Normal prolactin levels for adult males is less than 20 ng/mL.
Low prolactin on male hormone testing
There’s technically no minimum level of prolactin considered normal for adult males. Prolactin levels are generally low in cis men, so there are no symptoms of this condition.
High prolactin on male hormone testing
Overly high amounts of prolactin are present in up to 11% of infertile men, and may cause:
- reduced sex drive
- infertility
- milky discharge from the nipples
- erectile dysfunction
- larger breasts
- reduced sperm production
A prolactinoma, or a non-cancerous tumor in the pituitary gland, is a common cause of elevated prolactin levels. Other factors that can lead to increased prolactin include:
- certain medications
- hypothyroidism
- kidney disease
- other tumors near the pituitary gland
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
The pituitary gland makes thyroid-stimulating hormone, or TSH, in response to the level of thyroid hormones in your blood. TSH is responsible for telling the thyroid, a small gland at the front of the neck, to produce thyroid hormones. These hormones affect essential functions throughout your body.
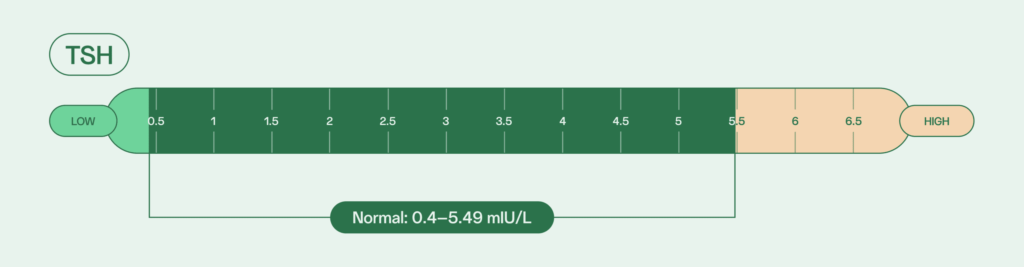
Normal TSH levels for adult males is between 0.4 and 5.49 mIU/L, depending on your age.
Low TSH on male hormone testing
The pituitary gland will reduce production of TSH if you already have high levels of thyroid hormone in your blood. This condition is called hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism can cause:
- weight loss
- fast heartbeat
- fatigue
- feelings of nervousness
- feeling weak
- sweating
- more frequent bowel movements
- enlarged thyroid, called goiter
Hyperthyroidism may also be linked to reduced semen volume, as well as lower sperm concentration, morphology, and motility.
High TSH on male hormone testing
On the other hand, if your thyroid hormone levels are too low, the pituitary gland will produce more TSH. With this condition, hypothyroidism, you may experience:
- weight gain
- fatigue
- depression
- sensitivity to cold
- joint pain
- thinning hair
- dry skin
- constipation
Hypothyroidism may also be associated with abnormal sperm morphology.
Understanding male fertility hormones and male-factor infertility
Many hormones impact male fertility, so abnormal levels of these hormones may affect your ability to conceive a child. Three male fertility hormones in particular must remain in balance to promote sperm production: LH, testosterone, and FSH.
For example,
- Since LH stimulates testosterone production, insufficient levels of it can lead to low levels of testosterone.
- Treatment of low testosterone may include testosterone replacement therapy.
- Injecting external testosterone reduces FSH, an important hormone for sperm production. As a result, the creation of new sperm and therefore your fertility may be impaired.
Which male fertility hormones should a male get tested for if he’s trying to conceive?
Hormone testing for infertility, or when testing for hormonal imbalances, uses blood tests to check whether your hormone levels are within the standard range.
If you’re trying to conceive, you’ll likely have your sperm production and fertility evaluated with a semen analysis and a male hormone test for FSH and testosterone. You may be tested for LH and prolactin, as well.
Who should do hormone testing
A hormone testing kit may help you identify issues that could affect your ability to conceive a child. This is important both for those who are planning to have a child and those who are experiencing difficulty conceiving.
You’ll also want to undergo testing for hormonal imbalance if you’re experiencing other symptoms of hormone imbalance, such as weight gain or loss, fatigue, low sex drive, or erectile dysfunction.
You may benefit from an FSH levels test, in particular, if you’ve been unsuccessful at conceiving a pregnancy for 12 months or if your sex drive is lower than usual.
Benefits of male hormone testing
Like a semen analysis, hormone testing is simple to perform and can give you key insights into your fertility and crucial male fertility hormones. If hormonal testing shows abnormal hormone levels, you can work with your doctor to identify treatment options or look for other ways to conceive, such as with assisted reproductive technology.
Treatment for male hormonal imbalance may include:
- Medication, such as testosterone therapy (not recommended if you’re trying to conceive) or clomiphene citrate
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss
- Treatment of tumors or gland problems that are contributing to hormone imbalance
Start with a semen analysis
If you’re curious about your fertility and ways to improve your sperm, the best place to begin is with a semen analysis. The test can even be done conveniently with an at-home semen analysis kit from Legacy, which also gives you options to preserve your sperm with short-term or long-term cryostorage.
Understanding the health of your sperm can help you recognize and seek treatment for underlying factors and take steps to protect your fertility for the future.