Guide to Sperm DNA Fragmentation
Sperm DNA fragmentation can lead to male-factor infertility, IVF failure, and miscarriage. But what exactly is sperm DNA fragmentation, and how does it affect fertility?
Sperm DNA fragmentation can be caused by a variety of factors, including illness, injury, lifestyle choices. This metric can be detected with a sperm DNA fragmentation test kit. Read on for our in-depth guide to sperm DNA fragmentation and how a sperm DNA fragmentation test kit can help.
Table of contents
- Why the genetic health of sperm is important
- What is sperm DNA fragmentation?
- Sperm DNA fragmentation and other semen parameters
- How sperm DNA fragmentation affects male fertility
- How sperm DNA fragmentation affects the health of the child
- What causes sperm DNA fragmentation?
- How to test for sperm DNA fragmentation
- References
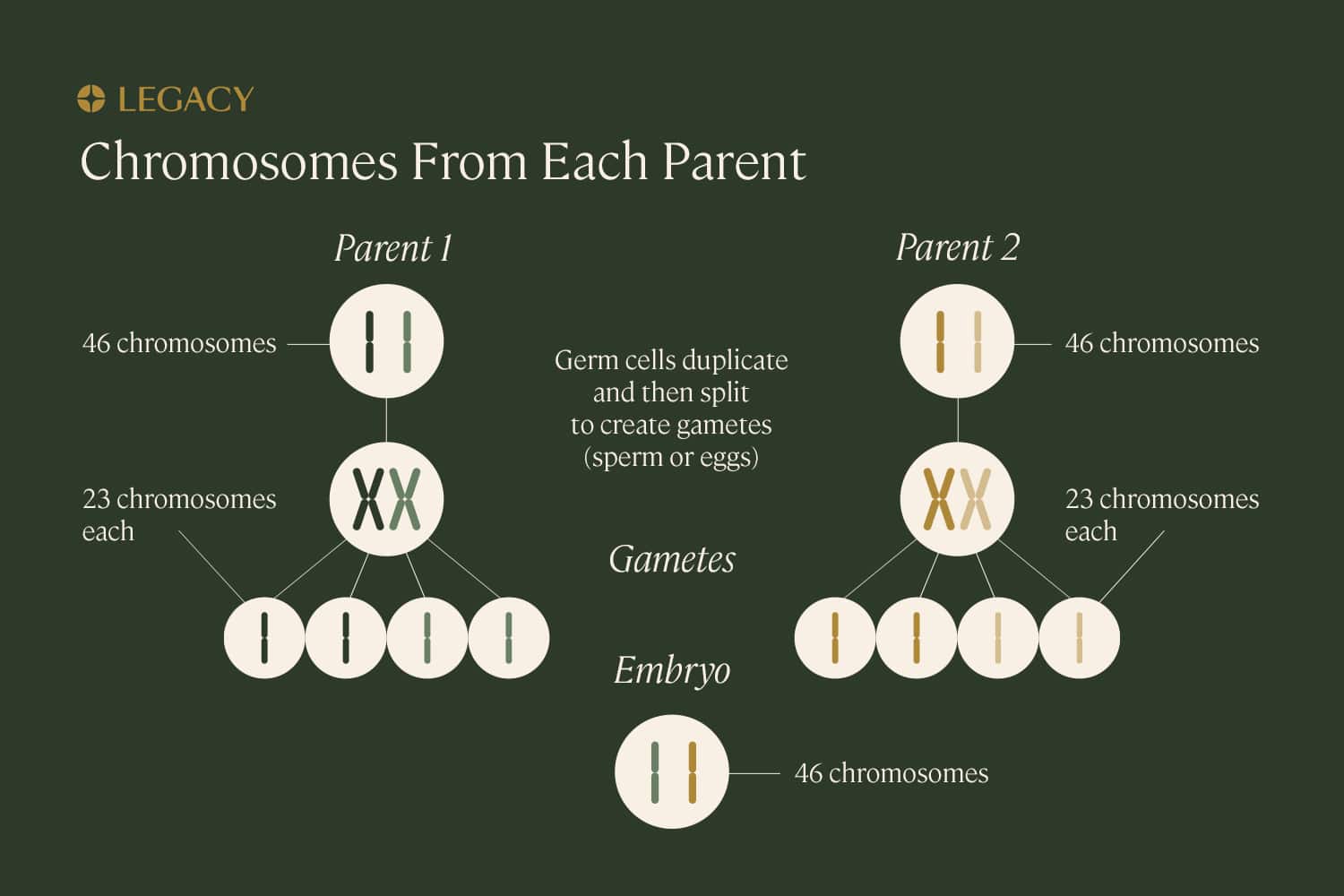
Why is the genetic health of sperm important?
The driving purpose of sperm is a single task: to carry genetic material (DNA) from one biological parent and combine with the genetic material contained within the egg of the other, creating a unique genetic code for the offspring.
Think about the structure of sperm. The majority of real estate is dedicated to its head, where chromosomes — molecules of DNA — are coiled tightly within a nucleus. The function of the neck and tail are to allow the sperm to transport its precious “cargo” most efficiently.
Since DNA carries all of the instructions for the development of an embryo, it makes sense that the genetic integrity of sperm is a key consideration in fertility. Any damage to the DNA within sperm may interfere with the sperm’s ability to properly fertilize an egg or develop into a healthy, thriving embryo. That’s exactly the issue with sperm DNA fragmentation.
Sperm DNA fragmentation is less often tested, and generally less well understood, than other semen parameters and sperm quality measures, such as sperm count, motility, and morphology.
But as research continues to clarify the relationship between sperm DNA fragmentation and birth rates, there’s an emerging belief among experts that sperm genetic integrity may be one of the most important factors for male fertility. As such, sperm DNA fragmentation test kits are particularly useful when trying to conceive.
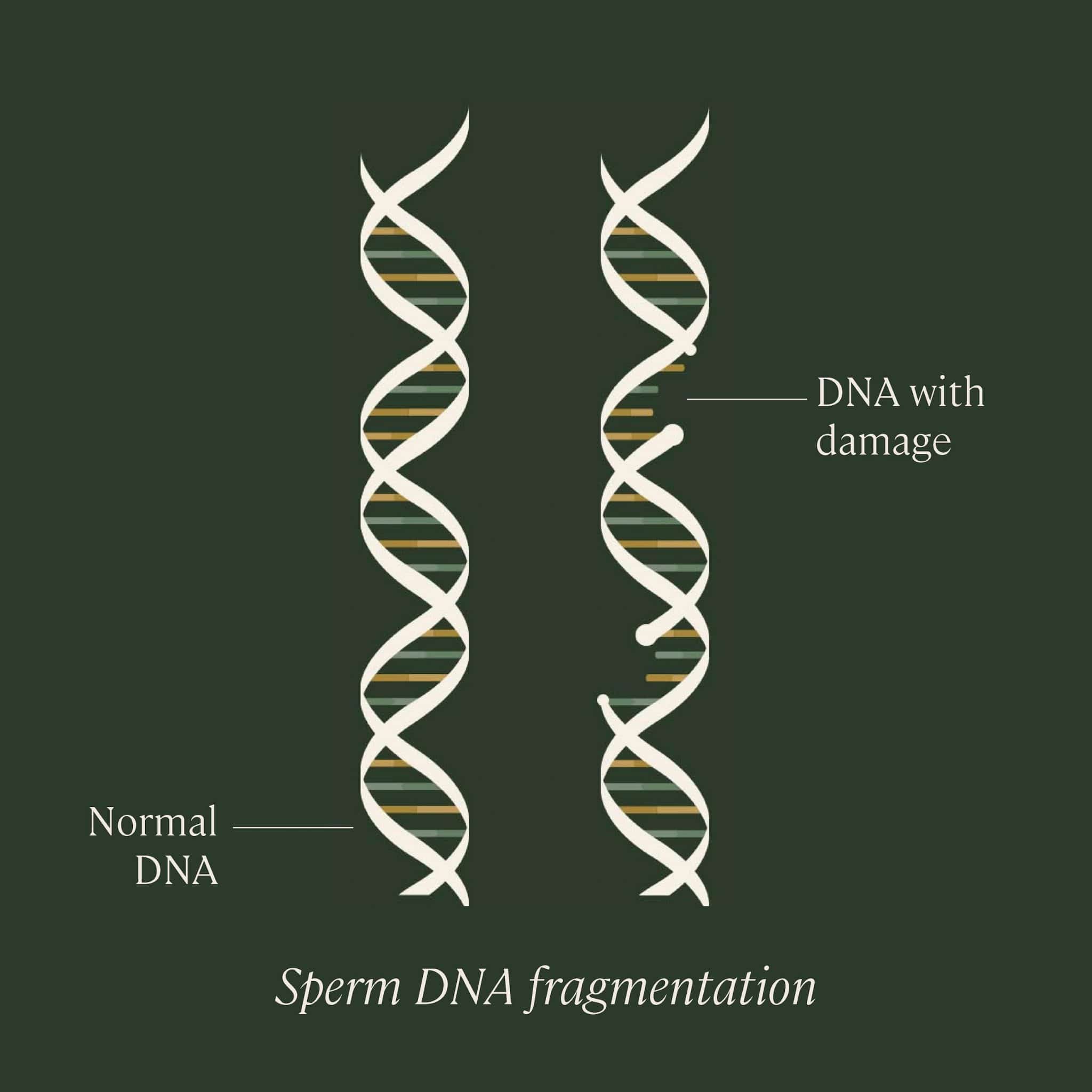
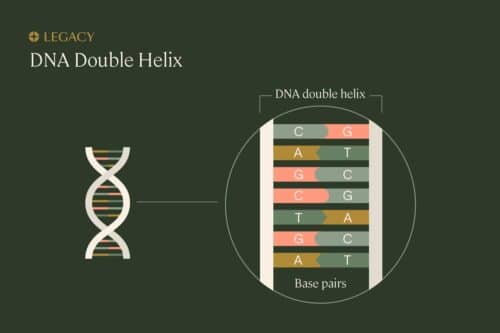
What is sperm DNA fragmentation?
In order to understand sperm DNA fragmentation, we first need to understand the proper structure of DNA. DNA is organized in a long, spiral staircase-like structure called a “double helix.” The steps of the staircase are made up of pairs of chemicals known as nucleotides; the different combinations of these base pairs are what create each organism’s unique genetic sequence. The nucleotides are bonded to each other, and to the long strands of sugars and phosphates that make up the “railings” of the staircase.
DNA is packaged into structures called chromosomes. While most cells within the human body contain 46 chromosomes, sex cells or “gametes” (eggs and sperm) contain just 23. When they combine, they create a fully realized organism with the proper number of chromosomes.
Sperm DNA fragmentation refers to a change or deletion of bases, or a break or separation in one or both strands of DNA contained within sperm. This damage can occur at several different points in the sperm’s life cycle: while it’s being produced within the testicles by a series of cell divisions called spermatogenesis, while it’s in “storage” in the epididymis prior to ejaculation, or even possibly post-ejaculation.
As sperm DNA fragmentation is not tested as part of a traditional semen analysis, sperm DNA fragmentation test kits play a crucial role.
Sperm DNA fragmentation: natural repair?
DNA damage is actually quite common in the human body, but most cells have the ability to identify and correct damage to their own genetic code. While immature sperm that are still in progress may have the ability to repair their own DNA to some extent, mature sperm do not.
Eggs can actually somewhat compensate for this. Upon fertilization, eggs have their own processes to repair errors in sperm DNA. But if the damage is too extensive (or if the egg is less able to perform this repair, possibly due to age) the damage can endure to the embryo stage.
The result may be the embryo’s failure to develop or implant (infertility), miscarriage (possibly recurring), or genetic abnormalities or illness within the offspring.

Understanding DNA fragmentation index
The term “DNA fragmentation index,” or DFI, refers to the percentage of sperm in a particular semen sample with fragmented DNA. A higher DNA fragmentation index means that a larger percentage of a person’s sperm contains genetic damage.
While experts disagree on specific cut-off values, generally speaking, a DNA fragmentation index over 30–50% is considered high, and may impact fertility. In some cases, subfertility may be experienced even among those with a DNA fragmentation index of 15–30%, especially if other abnormal semen parameters are present (such as low sperm count or poor motility or morphology), or the female partner is older.
Sperm DNA fragmentation testing is the most effective way to identify the DNA fragmentation index.
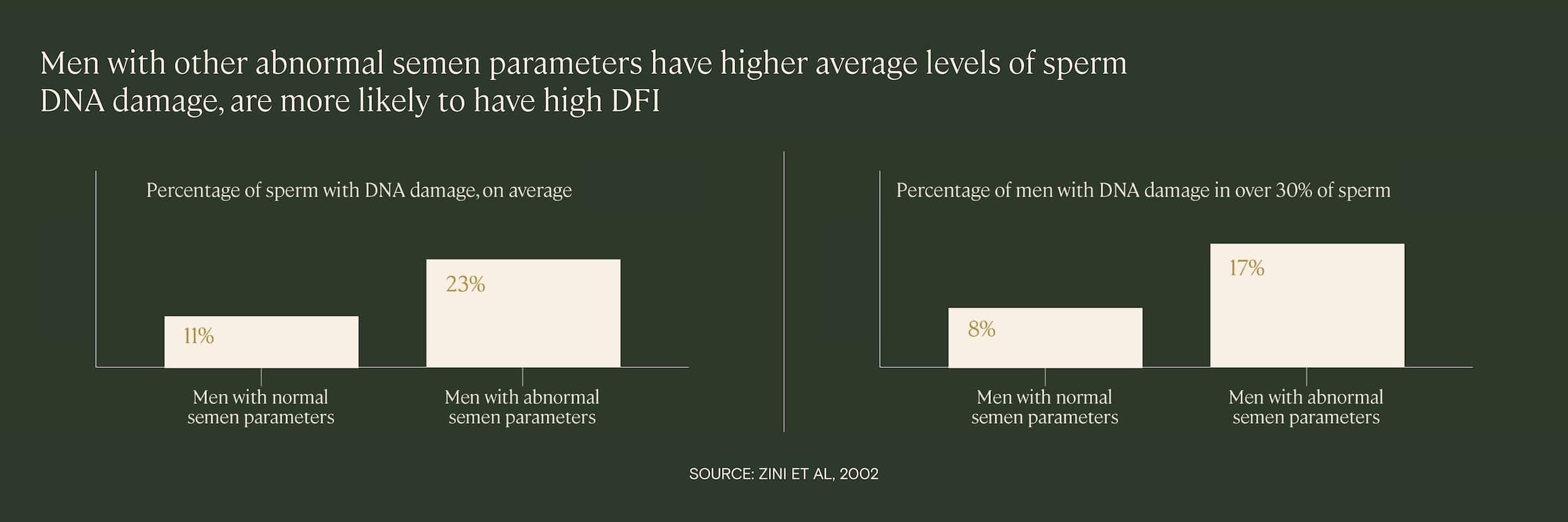
Sperm DNA fragmentation and other semen parameters
Research demonstrates that men who have high levels of sperm DNA fragmentation are also more likely to have other abnormal semen parameters, such as poor sperm motility or morphology. In one 2002 study of 88 infertile men, researchers found that the average level of DNA damage was significantly higher among those with other abnormal semen parameters.
This was confirmed in a 2009 study, in which higher sperm DNA damage was correlated with poorer semen parameters (sperm concentration, motility, morphology). Patients with abnormal results in all three categories had higher levels of sperm DNA fragmentation and were more likely to have a high DNA fragmentation index (over 30%) than patients with normal semen parameters.
This can be seen even in studies of those with just one problem with their sperm. In a 2014 study of 196 semen samples, it was found that men with teratozoospermia, a high level of abnormally shaped sperm, had a higher average DNA fragmentation index than men with normal sperm morphology.
That same year, another study of over a thousand infertile men with isolated sperm defects (meaning just poor motility, poor morphology, or low sperm count, and not a combination of the above) found that levels of sperm DNA fragmentation were significantly higher among men with poor sperm motility. Approximately 31% of those men had high sperm DNA fragmentation, defined in this study as over 30% DNA fragmentation index.
Why does this happen? It’s probable that the same underlying factors that contribute to abnormal semen parameters, such as advanced paternal age, smoking, or toxin exposure, also cause high levels of sperm DNA fragmentation. There may be other connections or mechanisms connecting these measures, as well.
This is important to understand because, as stated above, abnormal semen parameters can compound sperm DNA fragmentation issues. However, as we’ll explore below, high sperm DNA fragmentation can impact fertility even when not paired with other factors.
Sperm DNA fragmentation and male fertility
First, a note: conception is absolutely possible for those with high sperm DNA fragmentation. Even in studies that report lower pregnancy rates, longer time to conception, or higher miscarriage rates among men with a high DNA fragmentation index, researchers note that full-term pregnancies have been achieved.
That being said, studies demonstrate that men with high rates of sperm DNA fragmentation are at an increased risk for infertility. In one study, men presenting for infertility evaluation, who had not been able to achieve a pregnancy for a year or more, had, on average, over twice as many sperm with DNA fragmentation than fertile men (27.6% vs. 13.3%).
In another study, couples experiencing infertility or miscarriage were more likely to have a male partner with moderate or high levels of sperm DNA fragmentation. Researchers concluded that “spermatozoa with denatured DNA… were the best predictor for whether a couple would not achieve pregnancy.”
Sperm DNA fragmentation and fertility treatment
This trend — higher levels of sperm DNA fragmentation correlating with lower live birth rates — holds true even for those being treated for infertility with in vitro fertilization (IVF).
In one study of 360 couples undergoing IVF, higher sperm DNA fragmentation levels were associated with lower fertilization rates, embryo quality, and pregnancy rates. The couples who were not able to achieve pregnancy had an average of 51.7% sperm with DNA fragmentation, as opposed to 39.5% in the pregnant couples. The researchers concluded that sperm DNA fragmentation “can predict ART [assisted reproductive technology] outcome.”
This study was especially valuable because, other than sperm DNA fragmentation results, there were few significant differences between the group that achieved clinical pregnancy and the group that didn’t. The sperm count, motility, semen volume, and other parameters were all basically equivalent between the two study groups. This suggests that sperm DNA fragmentation impacts fertility independently of other semen parameters.
In another study of IVF cycles, researchers found a significant negative correlation between DNA fragmentation index and live birth rate. Specifically, implantation rates (the percentage of embryos that implant into the uterine lining for pregnancy) were lower for couples in which the male partner had a DNA fragmentation index of 30% or above. Those couples had an implantation rate of just 11.7%, compared with the 22.6% for couples in which the male partner had a DNA fragmentation index of less than 30%.
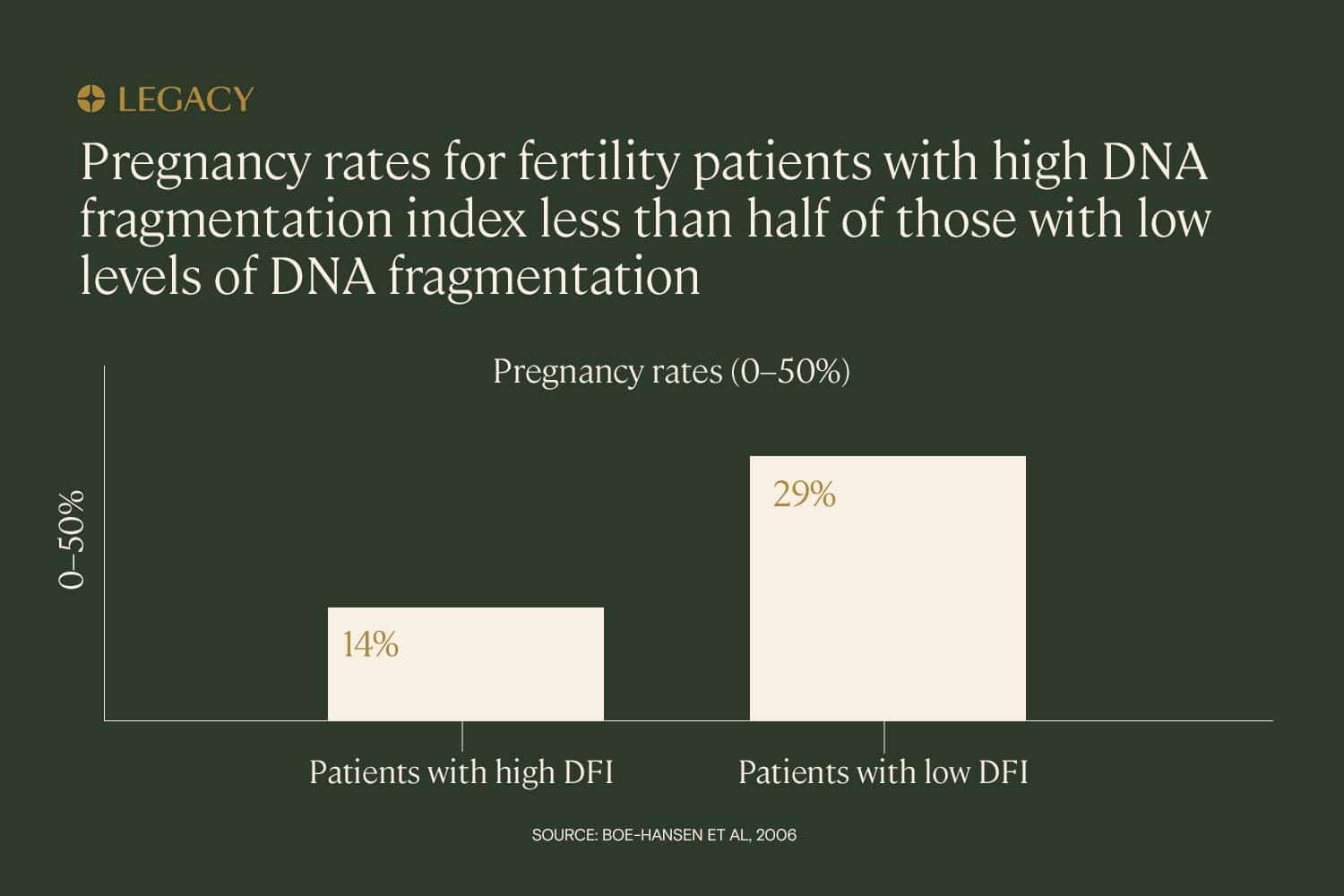
The trend appears to hold across different types of fertility treatment. In a study of IUI (intrauterine insemination), IVF, and ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection, a treatment in which a single sperm is injected directly into the egg), it was found that high DNA fragmentation index — defined as over 27% — had the power to predict whether or not a couple would achieve pregnancy. In this study, pregnancy rates for couples with high DNA fragmentation index were less than half that of low-DFI couples (14% vs. 29%).
Sperm DNA fragmentation and embryo quality
Embryo quality is a term used in fertility medicine. It’s a way of “grading” the health and development of an embryo created in the lab.
There are several different methods used to score embryo quality, but most examine the number of cells, cell size, and rate and pattern of cell division, in order to predict the likelihood that the embryo will implant and become a healthy baby. Embryo quality may also refer to embryo genetic health (having the proper number of chromosomes).
In many cases of high sperm DNA fragmentation, embryos fail early, during the 4- to 8-cell stage. Researchers note that sperm DNA integrity can cause “difficulty reaching the blastocyst stage.”
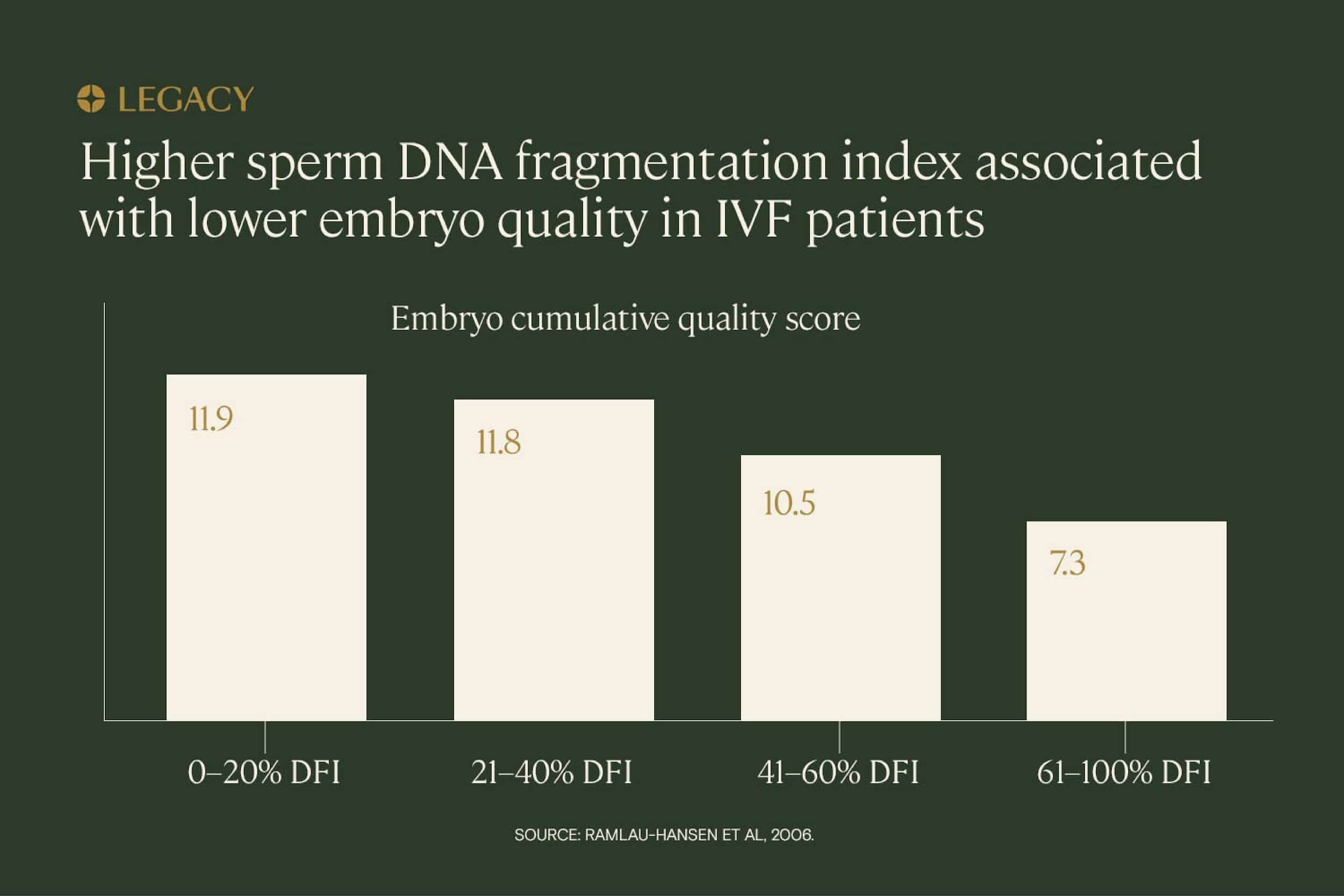
Past that point, there’s some evidence that high sperm DNA fragmentation is correlated with lower embryo quality scores, but research results are mixed. In a study of IVF patients, increasing DNA fragmentation indexes were associated with lower embryo scores. Those with a DNA fragmentation index above 60% scored approximately half as well as those with a DNA fragmentation index of less than 20%.
In another study of 286 embryos created with IVF, there were several important correlations: higher sperm DNA fragmentation was associated with higher embryo aneuploidy (genetically abnormal embryos), and increasing paternal age was associated with both. For men over 50, sperm DNA fragmentation rates were around 40%, and less than 30% of embryos created from their sperm were genetically normal.
But in a review of 28 studies analyzing the relationship between sperm DNA fragmentation and embryo quality, only 11 studies found a clear correlation between DNA damage in sperm and the genetic health or development of the embryo. In the remaining 17 studies, no relationship could be identified.
Sperm DNA fragmentation and miscarriage
Research indicates that sperm DNA damage is associated with pregnancy loss, especially early pregnancy loss, and may be implicated in recurrent miscarriage as well.
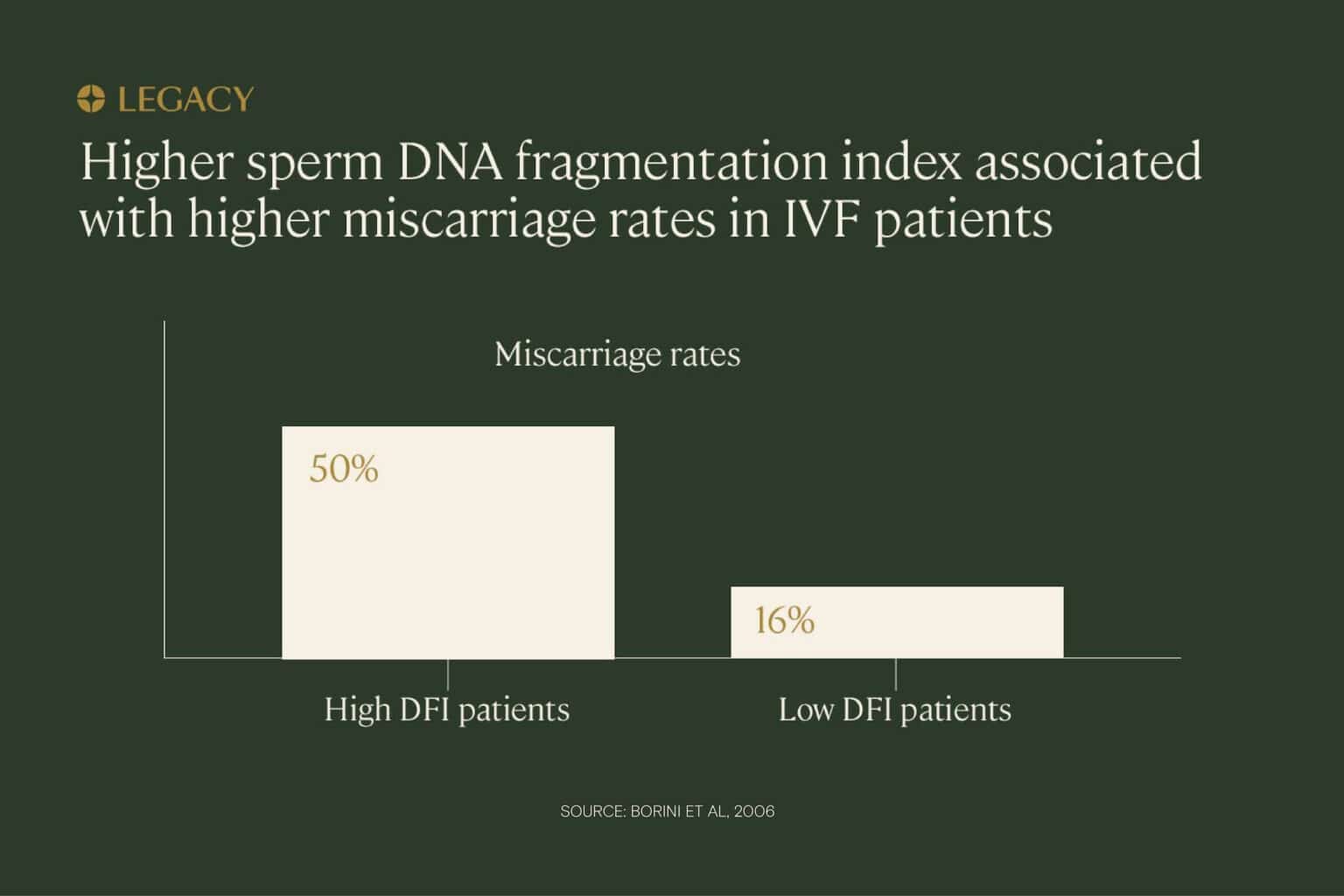
In one study of IVF patients, couples in which the male partner had high levels of sperm DNA fragmentation were significantly more likely to experience miscarriage compared to couples in which the male partners had low sperm DNA fragmentation rates (50% miscarriage rate vs. 16%). The same study also found that pregnancy rates were lower for high DNA fragmentation index patients. Researchers concluded that “high sperm DNA fragmentation can compromise ‘embryo viability,’ resulting in pregnancy loss.”
In another study, high DNA fragmentation index (defined in this case as over 27%) was again correlated with higher miscarriage rates. In this study, miscarriage rates for high-DFI couples was approximately 27%, as opposed to 10% for low-DFI couples. And again, in a third study of IUI patients, the early miscarriage rate for high DNA fragmenation index couples (over 30%) was 27%, compared to 8% for the low-DFI couples.
Sperm DNA fragmentation and
recurrent miscarriage
While it’s not entirely clear that sperm DNA fragmentation causes recurrent pregnancy loss (defined as two or more consecutive miscarriages), research demonstrates that the two issues are correlated.
In one study, 45% of male partners in cases of recurrent pregnancy loss had high sperm DNA fragmentation levels, compared to just 15% of the control group. In another, couples experiencing recurrent miscarriage were more likely to have male partners with high rates of sperm DNA damage. Researchers concluded that the genetic integrity of sperm was a “significant predictor for future [miscarriage] and infertility.”
A sperm fragmentation test kit, along with a semen analysis, can help you gain a comprehensive understanding of your sperm health before trying to conceive.
Sperm DNA fragmentation and the health of the child
Because of the many factors that contribute to the development of disease, it’s complicated to conduct research into specific causes. Some experts believe that “loss of sperm DNA integrity not only impacts reproductive and psychological health of the infertile couple but also increases childhood disease burden,” and that healthy sperm DNA is essential for “the health and well being of the next generation.” But the links are difficult to make conclusively.
A strong correlation has been found between the development of retinoblastoma, a childhood eye cancer, and DNA damage in paternal sperm. Researchers found that DNA fragmentation index levels were significantly higher in the sperm of fathers of children with retinoblastoma.
It’s also been shown that advanced paternal age has been associated with many conditions in offspring, possibly due to increased sperm DNA fragmentation with age. These conditions include:
- Cleft palate
- Heart defects
- Schizophrenia
- Autism
- Epilepsy
What causes sperm DNA fragmentation?
There are a few possible ways that sperms’ genetic material becomes damaged, and it can happen at several points in the process of producing and storing sperm.
Errors or damage during “condensation”
During spermatogenesis (the sperm production process), the genetic material within sperm condenses. The DNA wraps around a few specific proteins to organize itself snugly in the sperm’s head. This allows large amounts of DNA to occupy a very small space, and may protect the DNA from damage.
But this process also has the potential to introduce damage. Firstly, it’s quite a large amount of genetic material that needs to be compacted tightly within the nucleus of the sperm. It’s possible that this twisting could cause physical breaks in the DNA.
Additionally, if there are problems with the mechanisms that package this genetic material, such as a lack of the proteins required to facilitate the condensation process, DNA will be more susceptible to damage from outside forces.

Oxidative
stress
Free radicals, also known as reactive oxygen species (ROS), are unstable molecules produced as natural byproducts of daily life. At low levels, ROS are not typically damaging and may even be useful to cells. But if left unchecked, free radicals can cause damage to other molecules inside our cells, such as DNA. This damage is known as “oxidative stress.”
Our bodies typically use compounds called antioxidants to neutralize these molecules and prevent damage. Antioxidants are produced naturally by our body and absorbed from food or supplements. In fact, semen is known to contain relatively high quantities of antioxidants such as vitamin E, vitamin C, and glutathione, to protect sperm from oxidative stress. Antioxidants are also produced in other parts of the male reproductive system, including the epididymis, where sperm is stored.
There are certain experiences or behaviors that can cause levels of free radicals to rise beyond what our body can typically handle. Causes of oxidative stress include:
- Exposure to environmental toxins such as pesticides, heavy metals, or pollution
- Radiation
- Infections
- Smoking tobacco
- Drinking alcohol
On the other hand, if levels of antioxidants are too low, possibly due to a poor diet, they won’t be able to adequately counteract free radicals.
Researchers believe that oxidative stress is the major cause of sperm DNA fragmentation. In research, it’s been shown that as oxidative stress increases, sperm exhibit elevated levels of DNA damage. At the highest levels of oxidative stress, high DNA fragmentation index can be observed alongside a loss of sperm motility.
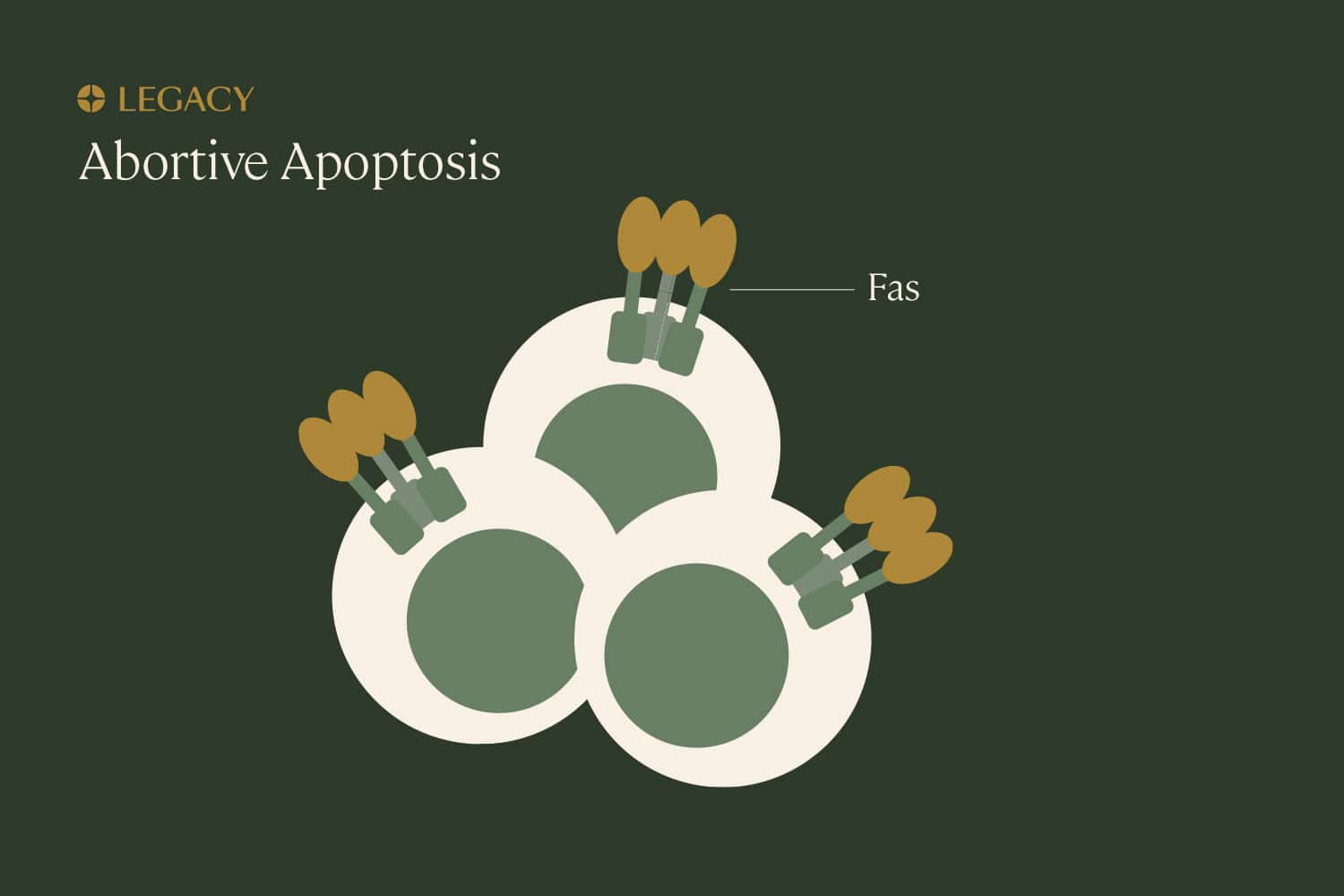
Abortive
apoptosis
Apoptosis is programmed cell death that’s part of normal growth and development. Think of it as a “self-cleaning” mechanism that eliminates unnecessary, damaged, or infected cells from the body. Though apoptosis involves the death of cells, it’s beneficial and important for the health of the overall organism. A cell that’s been marked for “deletion” can be identified by the presence of a specific protein, Fas, that induces apoptosis.
If the body is constantly cleaning out faulty cells, how do sperm cells with DNA damage make it into the semen? It seems that, sometimes, the body can recognize sperm with DNA damage and “earmark” them with Fas, but the process gets interrupted somewhere along the way, and damaged sperm are able to escape. This is known as abortive apoptosis.
Why this happens is not entirely clear, but we know it has an impact on fertility. In one study, men with abnormal sperm parameters display higher levels of Fas on their sperm.

These
mechanisms work together to cause sperm DNA fragmentation
These mechanisms are interrelated. It’s likely that, as opposed to a single one of these processes causing sperm DNA fragmentation, it’s a series of failures that results in high levels of DNA damage.
For example, if the DNA within sperm is not packaged correctly, it’s more vulnerable to oxidative stress. Too-low levels of antioxidants allow oxidative stress to damage sperm, and finally, the body fails to completely eliminate these damaged cells.
Risk factors for sperm DNA fragmentation
There are certain elements of a person’s medical history or lifestyle that may impact how likely they are to have high sperm DNA fragmentation. Here are a few of the key risk factors.
Paternal
age
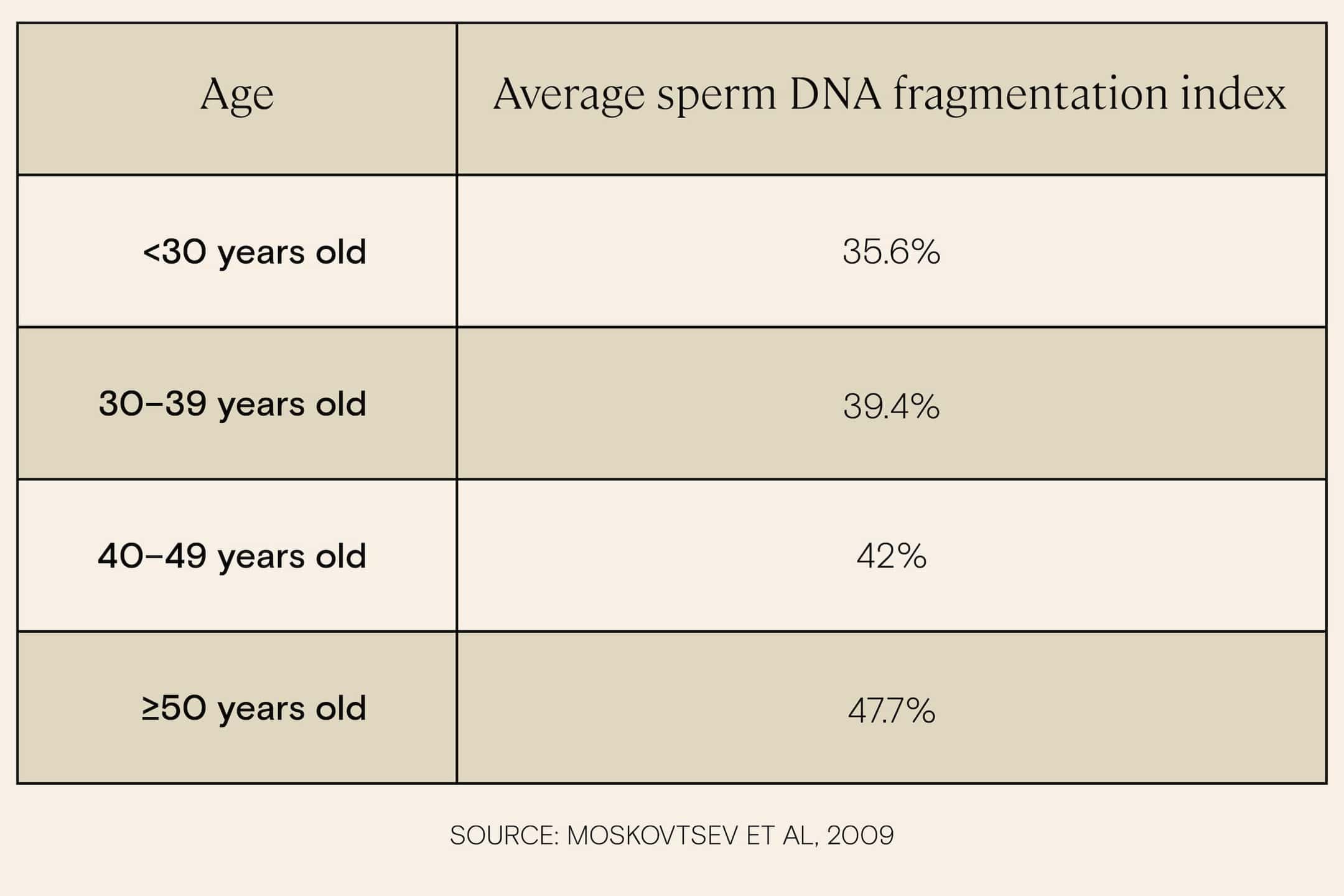
Research indicates that increasing age is associated with increased sperm DNA fragmentation, and the increase becomes especially significant for men in their late 40s and early 50s. One study of over 2,500 subjects found that while men under age 30 had an average DNA fragmentation index of 35.6%, men over 50 had an average DNA fragmentation index of 47.7, a level that is likely to come with impacts on fertility.
Another study of 2,681 male patients in Chile found a similar result: men over the age of 50 were more than four times more likely to present sperm DNA fragmentation than men under 30.
Why does this happen? There are several hypotheses. With age, cells are less able to repair their own DNA damage, possibly resulting in the production of sperm with increased damage. Additionally, as men age, they accumulate DNA damage in their testes, as well (thanks to oxidative stress), which is believed to impact the sperm cells created.
The increased damage could also be due to the fact that there’s a lower number of cells that are integral to the production of sperm in the testicles with age, or that the mitochondria that power sperm cells are less effective with age.
Smoking
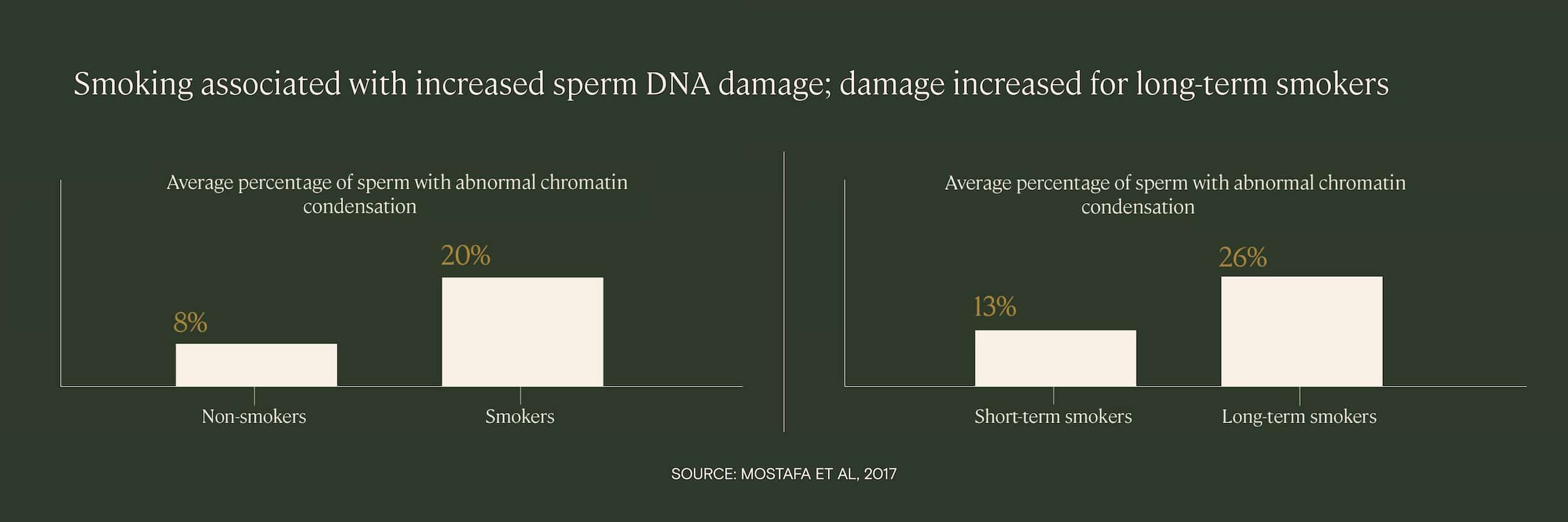
Cigarette smoking is a known cause of exposure to many damaging chemicals, such as cadmium and nicotine, as well as increased oxidative stress. Several studies have found that smokers have increased levels of sperm DNA fragmentation, and that the level of DNA damage is correlated with how long the patient has been a smoker and how many cigarettes they smoke.
In one study of infertility patients, researchers found that the percentage of sperm with abnormal DNA condensation was significantly higher among smokers than non-smokers, and that the abnormalities were proportional to both the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the duration of smoking.
In another study, researchers found that of four patient groups — a control group, an alcohol-drinking group, a cigarette-smoking group, and a drinking/smoking group — the two groups with smoking patients exhibited the highest average levels of sperm DNA fragmentation.
Drinking did appear to have a small impact on sperm DNA fragmentation, but smoking was much more impactful with regards to sperm DNA fragmentation.
Illness or
infection
Possibly because they increase oxidative stress, illness or infection is associated with increased sperm DNA fragmentation. These include:
- Influenza and other fever-inducing illnesses
- Cancer
- Sexually transmitted infections
In a study of men with sexually transmitted infections from chlamydia or mycoplasma (a bacteria that causes inflammation in the urinary tract), patients had increased DNA fragmentation index compared to controls (an average of 35% compared to 11%).
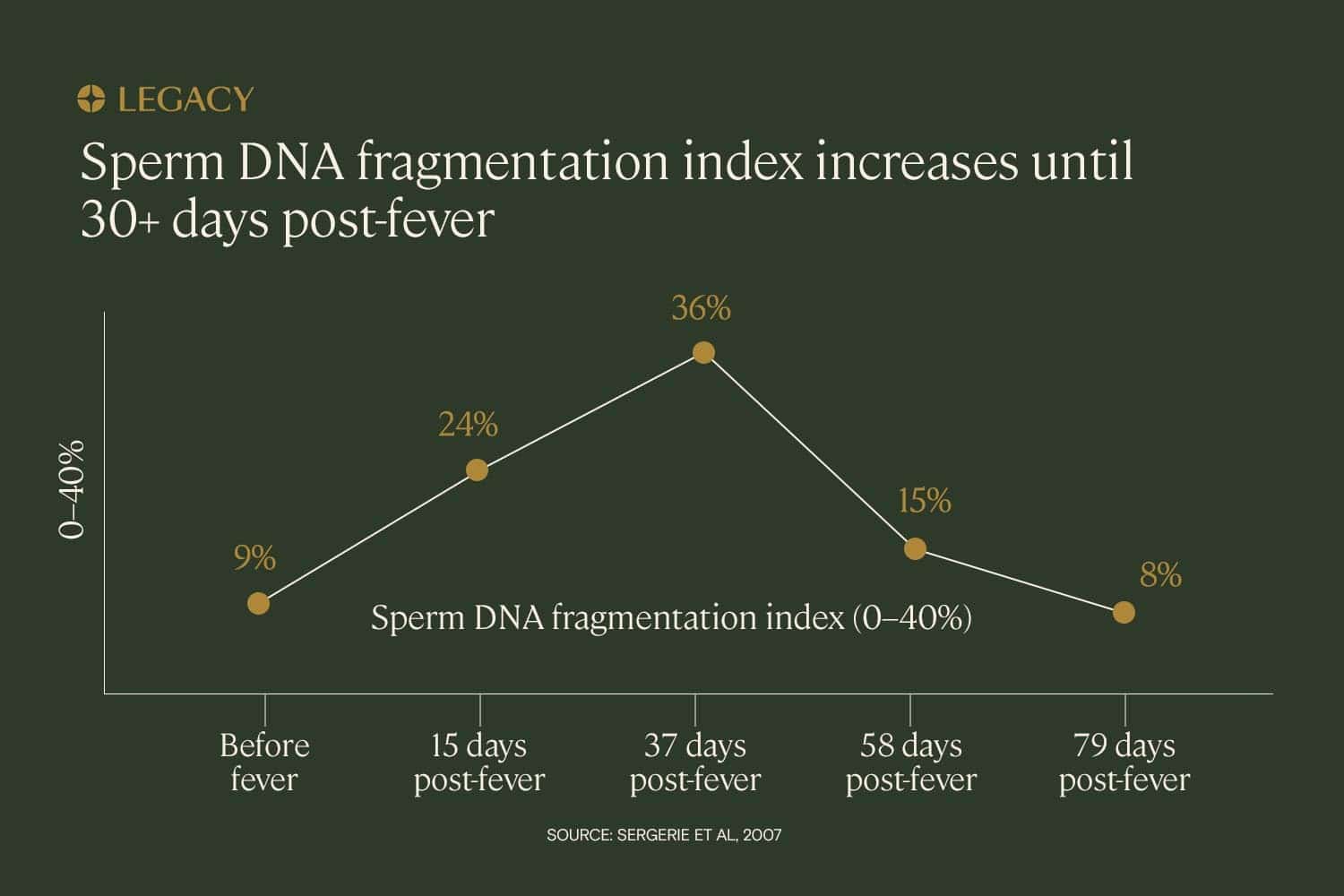
In a case study of one patient with a fever illness, sperm DNA fragmentation testing revealed that the DNA fragmentation index increased significantly in the month following the fever. DFI increased by 24% in the 15 days following the fever and 36% in the 37 days following, reflecting the infection and fever’s impact on the sperm that were in production at the time of the illness.
In this case study, the DNA fragmentation index did not decrease to normal levels until approximately 2–3 months after the fever resolved. This reflects the duration of spermatogenesis — it takes approximately 70–90 days to produce sperm.
And, while cancer treatment is well known for its impact on fertility (more on that below), research is revealing that cancer itself may have a damaging effect on sperm DNA. One study found that cancer patients had higher levels of sperm DNA fragmentation than infertile men, even before receiving any chemotherapy or radiation treatments.
Cancer treatment
Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation are life-saving, but may have the side effect of impacting fertility.
Chemotherapy works by using medications to identify fast-dividing cancer cells and kill them or prevent them from dividing. But because the medication is administered through the bloodstream to the entire body, it can also attack other cells, including sperm cells.
Research in male rats demonstrates that the chemotherapy medications most often used for testicular cancer are associated with an increase in sperm DNA fragmentation. A case study of a human cancer patient presented a similar impact, revealing a substantial increase in sperm DNA fragmentation after 8 weeks of chemotherapy treatment for leukemia that persisted nearly a year later.
Radiation therapy involves directing high-energy rays at the cancer, in hopes of killing those cells. But by extension, this treatment can also damage parts of the body surrounding the cancer as well, potentially slowing down or stopping sperm cell production.
Some men who undergo radiation will experience a temporary drop in fertility that recovers in the years following treatment. For others who undergo higher doses of radiation, sperm production may stop permanently. It’s been demonstrated in lab experiments that exposure to radiation creates a dose-dependent increase in sperm DNA fragmentation.
Up to 75% of reproductive-age men who are diagnosed with cancer may face infertility as a result of treatment, according to Livestrong. That’s why it’s highly recommended that men diagnosed with cancer freeze their sperm prior to treatment. Learn more about sperm freezing.
Alternatively, a sperm DNA fragmentation test kit can be used after treatment.
Chemical,
toxin, or radiation exposure
According to the CDC, exposure to a number of chemicals or heavy metals are known to cause DNA damage within sperm. Examples of chemicals that cause sperm DNA fragmentation include:
- Phthalates and styrene (chemicals used in plastic production)
- Pesticides/insecticides such as organophosphate, carbaryl, or fenvalerateL
- Lead
- Benzene, a chemical that’s widely used in manufacturing and also found in gasoline and tobacco smoke
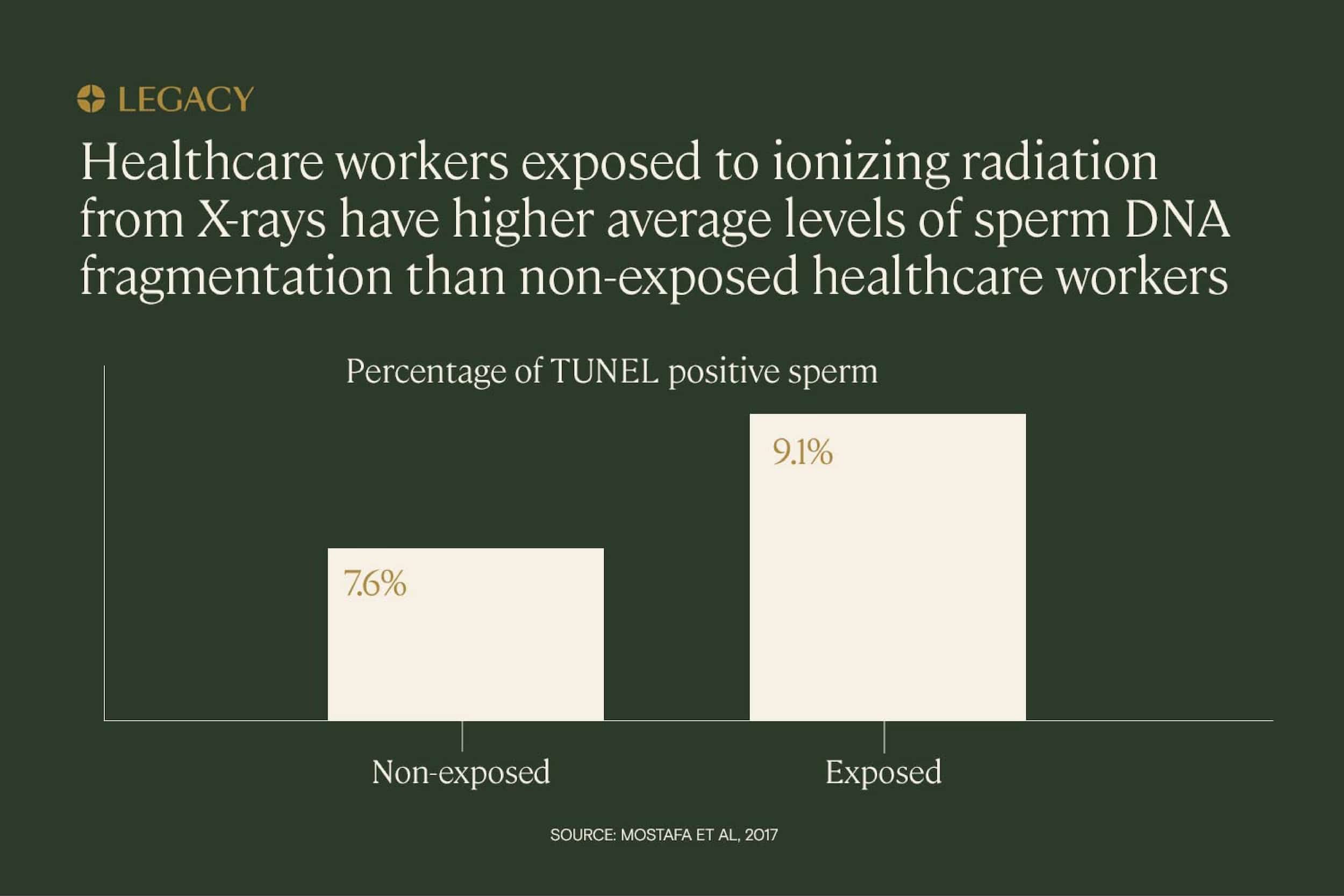
Radiation is also implicated in sperm DNA fragmentation. One study of healthcare workers exposed to ionizing radiation (used in X-rays) concluded that sperm DNA fragmentation levels were significantly higher among exposed men than among non-exposed men.
The most damaging long-term, repeated exposure is typically thanks to a person’s occupation. Healthcare workers, for example, have repeated long-term exposure to radiation, as illustrated above. Other occupations with exposure risk include jobs in manufacturing, agriculture, and the military.
How can sperm DNA fragmentation be tested?
Sperm DNA fragmentation is not tested as part of a typical semen analysis. However, a semen analysis along with a sperm DNA fragmentation test kit is a great way to get a complete picture of your overall sperm health.
There are several different tests that use different technologies to identify and quantify DNA damage within sperm:
- Sperm chromatin dispersion (SCD) testing. In this process, sperm are carefully denatured — or chemically degraded — and examined under a high-powered microscope to identify the “halos” formed by loops of intact DNA. (Sperm with damage will not produce a halo.)
- Single cell gel electrophoresis assay (SCGE), also known as the comet assay. In this process, the cell membrane around sperm is broken down. Fragmented strands of DNA form a “tail,” like that on a comet, the presence and size of which indicates damage to the genetic material.
- Sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA). This is a process in which sperm cells are stained and placed in the path of a laser beam. The laser will cause the dye to emit fluorescent light of a certain color: green indicates sperm with non-detectable levels of fragmented DNA, while yellow and red indicate moderate to high levels of sperm DNA fragmentation.
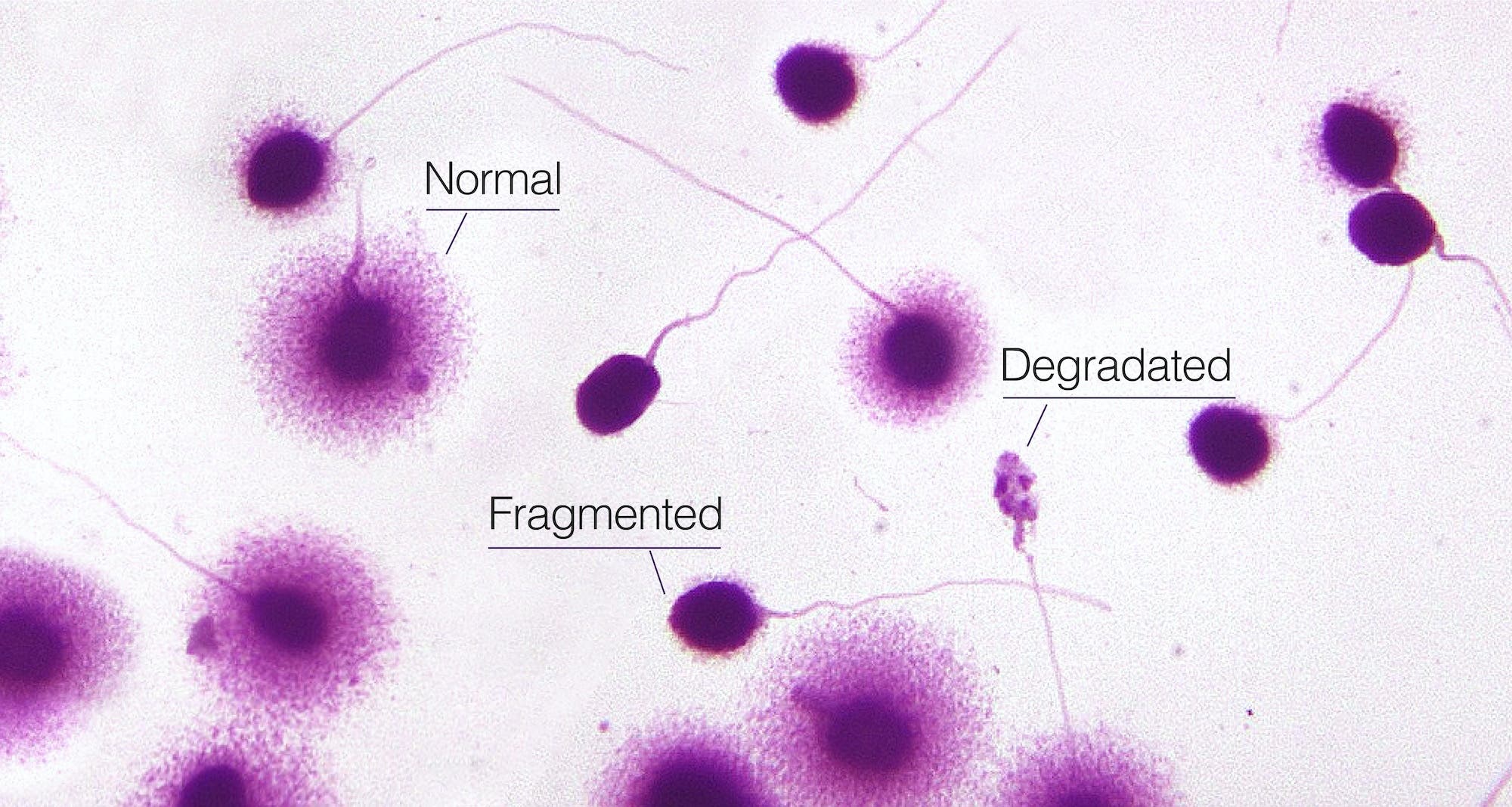
- Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. In this test, an enzyme that attaches to broken DNA strands is “tagged” with fluorescent dye and added to sperm cells. Under a laser light, the cells with DNA damage will emit a different color than those with intact DNA.
These tests are typically performed in a speciality lab. Even if you collect a semen sample at your fertility clinic, it will be shipped to the lab for sperm DNA fragmentation testing.
At-home sperm DNA fragmentation testing
Legacy has introduced the first and only easy mail-in sperm testing kit that can analyze sperm DNA fragmentation. Our labs use the Halosperm SCD technique to assess sperm genetic health.
At-home sperm DNA fragmentation test kits, early in the process, can be game-changing, allowing you to address abnormalities early or work with your doctor to choose the best treatment for you. Legacy’s sperm DNA fragmentation test kit makes this more accessible, affordable, and approachable.
Order your at-home sperm DNA fragmentation test kit.
When should sperm DNA fragmentation be tested?
Historically, sperm DNA fragmentation hasn’t been tested until a couple has gone through one or more failed fertility treatments. But that’s beginning to change, as researchers recognize the predictive power of DNA fragmentation index, and the impact of sperm DNA fragmentation on the health of offspring.
Now, experts are arguing that sperm DNA fragmentation should be tested universally, prior to starting any fertility treatments. As upwards of 15% of infertile men have normal semen analysis results, a more thorough evaluation of sperm health is essential, and sperm DNA fragmentation test kits can help.
Bottom line: There’s really no time that’s too early for testing. Especially because sperm DNA fragmentation may be treatable with lifestyle interventions, testing earlier in the fertility process can ultimately save time, energy, and money, and prevent you from undergoing more invasive procedures.

Who should be tested for sperm DNA fragmentation?
- All fertility patients, especially:
- Patients with unexplained infertility.
- Patients diagnosed with male-factor infertility of an unknown cause.
- Patients with a history of miscarriages.
- Patients with poor embryo quality during IVF treatment.
- Those over 40.
- Those with a history of cancer.
- Those under treatment with prescription medications.
- Those with lifestyle habits that may affect sperm health, such as smoking.
- Anyone who wants a more thorough understanding of their sperm health.
References
- Clara González-Marín et al. “Types, Causes, Detection and Repair of DNA Fragmentation in Animal and Human Sperm Cells.” International Journal of Molecular Science, 2012.
- Rima Dada. “Sperm DNA damage diagnostics: when and why.” Translational Andrology and Urology, 2017.
- Jordi Ribas-Maynou et al. “Single and Double Strand Sperm DNA Damage: Different Reproductive Effects on Male Fertility.” Genes, 2019.
- Armand Zini et al. “Prevalence of abnormal sperm DNA denaturation in fertile and infertile men.” Urology, 2002.
- Sergey I. Moskovtsev et al. “Sperm DNA damage: correlation to severity of semen abnormalities.” Urology, 2009.
- Javier García-Ferreyra et al. “Sperm DNA Fragmentation is Significantly Increased in Those Men with Morphologically Abnormal Spermatozoa.” Journal of Fertilization: In Vitro, IVF-Worldwide, Reproductive Medicine, Genetics & Stem Cell Biology, 2014.
- Stephanie Belloc et al. “Which isolated sperm abnormality is most related to sperm DNA damage in men presenting for infertility evaluation.” Journal of Assisted Reproduction & Genetics, 2014.
- Luke Simon et al. “Clinical significance of sperm DNA damage in assisted reproduction outcome.” Human Reproduction, 2010.
- L. Gandini et al. “Full‐term pregnancies achieved with ICSI despite high levels of sperm chromatin damage.” Human Reproduction, 2004.
- Aleksander Giwercman et al. “Sperm chromatin structure assay as an independent predictor of fertility in vivo: a case-control study.” International Journal of Andrology, 2010.
- D. P. Evenson et al. “Utility of the sperm chromatin structure assay as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in the human fertility clinic.” Human Reproduction, 1999.
- B. E. Speyer et al. “Fall in implantation rates following ICSI with sperm with high DNA fragmentation.” Human Reproduction, 2010.
- Gry Brandt Boe-Hansen et al. “The sperm chromatin structure assay as a diagnostic tool in the human fertility clinic.” Human Reproduction, 2006.
- Javier García-Ferreyra. “Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Its Relation With Fertility, New Discoveries in Embryology,” IntechOpen, 2015.
- Javier García-Ferreyra et al. “High Aneuploidy Rates Observed in Embryos Derived from Donated Oocytes are Related to Male Aging and High Percentages of Sperm DNA Fragmentation.” Clinical Medical Insights: Reproductive Health, 2015.
- Armand Zini et al. “Is sperm DNA damage associated with IVF embryo quality? A systematic review.” Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, 2011.
- A. Borini et al. “Sperm DNA fragmentation: paternal effect on early post-implantation embryo development in ART.” Human Reproduction, 2006.
- Ming-Huei Lin, MD et al. “Sperm chromatin structure assay parameters are not related to fertilization rates, embryo quality, and pregnancy rates in in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection, but might be related to spontaneous abortion rates.” Fertility & Sterility, 2008.
- Hongyi Yang et al. “The effect of sperm DNA fragmentation index on assisted reproductive technology outcomes and its relationship with semen parameters and lifestyle.” Translational Andrology and Urology, 2019.
- Ines Zidi-Jrah, MD et al. “Relationship between sperm aneuploidy, sperm DNA integrity, chromatin packaging, traditional semen parameters, and recurrent pregnancy loss.” Fertility & Sterility, 2016.
- Lihong Zhang et al. “Sperm chromatin integrity may predict future fertility for unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion patients.” International Journal of Andrology, 2012.
- Surabhi Gautam et al. “Sperm DNA damage in non-familial sporadic heritable retinoblastoma (NFSHRb).” Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 2015.
- Surabhi Gautam et al. “Childhood disease burden: Is father to blame?: Beyond the Abstract.” Urology Today, 2018.
- R. John Aitken at al. “Apoptosis and DNA damage in human spermatozoa.” Asian Journal of Andrology, 2011.
- Gabriele Pizzino et al. “Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health.” Oxidative Medicine & Cell Longevity, 2017.
- Sedigheh Ahmadi, M.Sc. et al. “Antioxidant supplements and semen parameters: An evidence based review.” International Journal of Reproductive Biomedicine, 2016.
- C. Wright et al. “Sperm DNA damage caused by oxidative stress: modifiable clinical, lifestyle and nutritional factors in male infertility.” Reproductive Biomedicine Online, 2014.
- R. J. Aitken et al. “Relative impact of oxidative stress on the functional competence and genomic integrity of human spermatozoa.” Biology of Reproduction, 1998.
- Denny Sakkas et al. “Abnormal spermatozoa in the ejaculate: abortive apoptosis and faulty nuclear remodelling during spermatogenesis.” Reproductive Biomedicine Online, 2003.
- Victor Pino et al. “The effects of aging on semen parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation.” JBRA Assisted Reproduction, 2020.
- R. M. Mostafa et al. “The effect of cigarette smoking on human seminal parameters, sperm chromatin structure and condensation.” Andrologia, 2017.
- S. Aboulmaouahib et al. “Impact of alcohol and cigarette smoking consumption in male fertility potential: Looks at lipid peroxidation, enzymatic antioxidant activities and sperm DNA damage.” Andrologia, 2018.
- Guadalupe Gallegos, MD et al. “Sperm DNA fragmentation in infertile men with genitourinary infection by Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma.” Fertility & Sterility, 2008.
- Martin Sergerie, PhD et al. “High risk of temporary alteration of semen parameters after recent acute febrile illness.” Fertility & Sterility, 2007.
- Marcos Meseguer, PhD et al. “The effect of cancer on sperm DNA fragmentation as measured by the sperm chromatin dispersion test.” Fertility & Sterility, 2008.
- Géraldine Delbes et al. “Effects of the chemotherapy cocktail used to treat testicular cancer on sperm chromatin integrity.” Journal of Andrology, 2007.
- R. Chatterjee et al. “Testicular and sperm DNA damage after treatment with fludarabine for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.” Human Reproduction, 2000.
- Ian D. Morris. Sperm DNA damage and cancer treatment.” International Journal of Andrology, 2002.
- Dayanidhi Kumar et al. “Semen Abnormalities, Sperm DNA Damage and Global Hypermethylation in Health Workers Occupationally Exposed to Ionizing Radiation.” PLoS One, 2013.
- Li-hong Zhang, MSc et al. “Measurement of sperm DNA fragmentation using bright-field microscopy: comparison between sperm chromatin dispersion test and terminal uridine nick-end labeling assay.” Fertility & Sterility, 2009.