If you’re prescribed testosterone, you may be wondering about this potential “perk.” And if you’re trying to increase penile size, you might be looking at your options. So, can testosterone increase size, particularly in adulthood? What about TRT for penile growth? What’s the connection between testosterone and penis size? Here’s what science says.
Key takeaways
- Testosterone is a hormone responsible for many traditionally “male” features, including the growth of your penis in utero.
- However, for adults, taking testosterone won’t increase penile size. It can reduce erectile dysfunction and make the penis feel harder (if not actually bigger).
- Testosterone replacement therapy may be prescribed to treat abnormally low testosterone levels. TRT can have side effects, including infertility.
What is testosterone?
Testosterone is the main sex hormone in men. In utero, it’s responsible for the development of the penis and testicles. Later, it drives the development of typically male secondary sexual characteristics at puberty: a deeper voice, body hair, muscle growth, and sperm production. Testosterone also helps maintain many bodily processes and features throughout life, including libido, muscle mass, bone strength and growth, and mood.
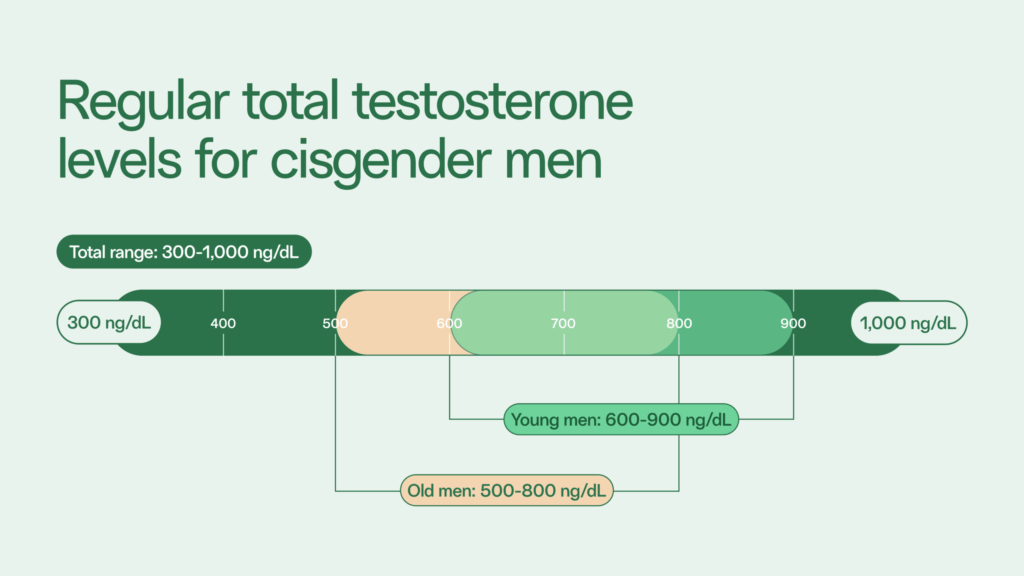
If you have low T, your healthcare provider may prescribe testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). TRT increases the amount of testosterone in a man’s blood using a synthetic form of testosterone that’s manufactured in a lab.
There’s no question that testosterone is involved in sexual development and sex drive. But even testosterone has its limits, especially when it comes to penis enlargement or TRT penile growth.
Will taking testosterone increase my penis size?
Sorry, but once you’ve reached adulthood, no. During puberty, testosterone causes the penis and testicles to grow to their adult size. But once puberty ends — usually by age 18 — taking testosterone won’t cause your penis to grow any further.
Penis size is largely determined by genes (although other factors, such as exposure to hormones and chemicals during gestation, can play a role). Essentially, the ceiling on your penis size is pre-programmed.
In specific cases, before puberty hits, testosterone therapy may be used to increase penis size. Testosterone has been used to treat pediatric patients with micropenis, a penis that’s significantly smaller than average for their age. One study found that intramuscular injections of testosterone allowed penile growth to “catch up” to a normal range.1
But this has only been observed before puberty. Multiple studies have found that testosterone treatment after puberty doesn’t result in penile growth.
Testosterone and erectile dysfunction
Maybe you’re not looking to get bigger, just harder. Abnormally low testosterone can cause erectile dysfunction (ED), difficulty getting or staying hard. If you have ED that’s related to low T, testosterone supplementation may make your penis seem bigger thanks to improved erectile strength.
Learn more about erectile dysfunction and fertility.
Does penis size correlate with testosterone levels or fertility?
Not directly. People with large penises can have low T or a low sperm concentration, and people with small- to average-sized penises can have testosterone and sperm-concentration levels that are off the charts. And while a 2021 study found that bigger penises were tied to better fertility, it was the only study that came to this conclusion — and the difference between fertile and infertile men’s average penis size was just 1.1cm.
One caveat: the penis and testicles can shrink with age, and that’s partly caused by the natural decline in testosterone production. Testosterone levels drop with age, about 1–2% per year.2 After the age of 45, more than 1 in 3 men have an abnormally low testosterone level (commonly known as “low T”).
This can cause some uncomfortable symptoms of low testosterone, including fatigue, low libido, erectile dysfunction, weight gain, loss of muscle or bone mass, and depression. Additionally, older men have lower sperm quality, likely as a result of reduced testicular function.
Effects of testosterone therapy
While testosterone therapy might not make your penis bigger, it has been shown to improve:
- Sex drive and sexual function
- Mood and energy levels
- Body weight and composition (fat vs. muscle mass)
- Bone mass
- Insulin resistance
Testosterone replacement therapy can also have unwanted side effects, including: acne, sleep apnea, swelling of the ankles and breasts, higher risk of blood clots, and infertility.
Read what to expect when you’re starting TRT.
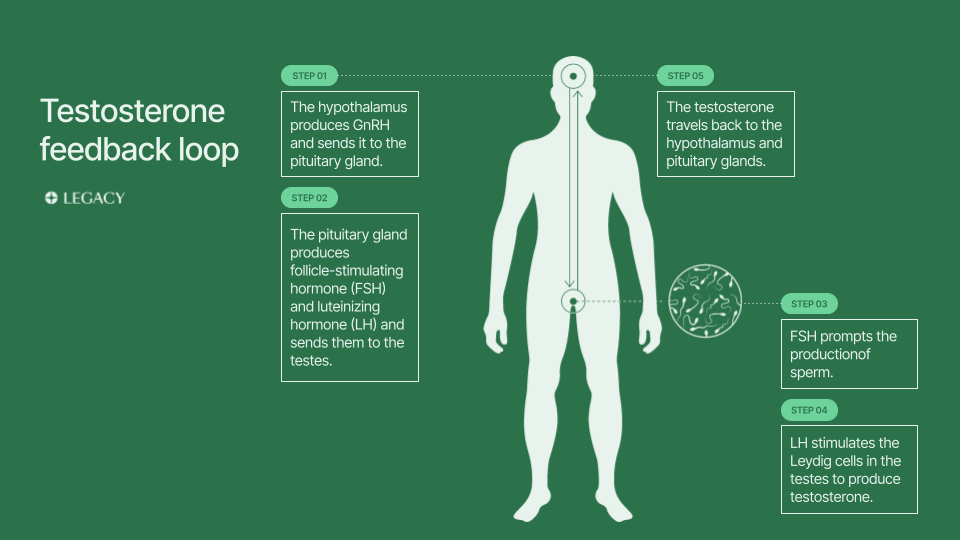
Testosterone therapy and sperm health
Many men are surprised to learn that taking T will cause infertility. But it’s true — adding external testosterone to the body can cause the brain to slow or stop making the hormones that drive male fertility. This can reduce or curtail sperm production, also known as spermatogenesis. Research has shown that the majority of men who take TRT will be infertile within a few months.
Stopping TRT may allow sperm production to resume. But that can be a slow process, and it isn’t guaranteed. About 1 in 3 men on TRT don’t recover sperm production within 1 year, and in 10% of men who go on TRT, sperm production never resumes.3
If you’re considering testosterone replacement therapy and might still want to have biological children someday, it’s a good idea to freeze your sperm before you begin. The process is easy, and it can give you peace of mind while you pursue relief from the symptoms of low T.
Learn more about why you should freeze your sperm before TRT.
References
2. Stanworth. “Testosterone for the aging male; current evidence and recommended practice.” 2008.